LOG307 Report: Optimization and Simulation for Production Planning
| University | Singapore University of Social Science (SUSS) |
| Subject | Optimisation and Simulation for Decision-Making |
Guidelines:
You are required to submit only an Excel file.
Use separate sheets to answer different questions and name the sheets accordingly.
Use a textbox to write your answers in the Excel sheet.
Question 1
Grayson Displays manufactures two types of shelves for retail stores. Model A is the standard model, while Model HD is a heavy-duty version. Shelves are manufactured in three major steps: stamping, forming, and assembly. In the stamping stage, a large machine is used to stamp (i.e., cut) standard sheets of metal into appropriate sizes. In the forming stage, another machine bends the metal into shape. Assembly involves joining the parts with a combination of soldering and riveting. Grayson’s stamping and forming machines work on both models of shelves. Separate assembly departments are used for the final stage of production. The hours required on each machine for each unit of product are shown in Table 1.
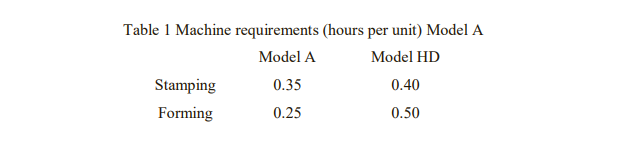
Both the stamping and forming machines can operate for 1,000 hours and 800 hours each month, respectively. The Model A assembly department has a monthly capacity of 2,000 units. The Model HD assembly department has a monthly capacity of only 1,500 units. Currently, Grayson is producing and selling 400 units of model A and 1,400 units of Model HD per month.
Model A shelves are sold for $1,800, and Model HD shelves are sold for $2,500. Grayson Displays’ operation is fairly small in the industry, and management at Grayson believes it cannot raise prices beyond these levels because of the competition. However, the marketing department believes that Grayson can sell as much as it can produce at these prices. The overhead costs for different operations are shown in Table 2.
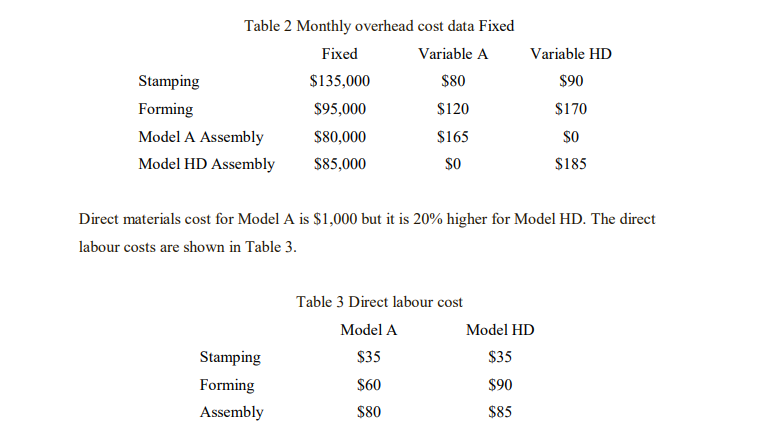
Management at Grayson just met to discuss next month’s operating plan. Although the shelves are selling well, the overall profitability of the company is a concern. Tom, the plant’s engineer, suggested that the current production of Model A shelves be cut back. According to Tom, “Model A shelves are sold for $1,800 per unit, but our costs are $1,832. Even though we’re selling only 400 units a month, we’re losing money on each one. We should decrease the production of Model A”.
Rachel, the controller, disagreed. She said that the problem was the Model A assembly department was trying to absorb a large overhead with a small production volume. “The Model A units are making a contribution to overhead. Even though production doesn’t cover all of the fixed costs, we would be worse off with lower production”.
Question 1a
Apply linear programming to determine the monthly production for the two shelves for the upcoming month. Clearly define all necessary variables and notations. Specify the input variables, constraints, and objective function in detail. (20 marks)
Question 1b
Convert the LP model into a spreadsheet model. Clearly identify the input variables, constraints, and objective function in the spreadsheet. Show the calculations. Solve the LP problem using the Solver. Provide a screenshot of the Solver settings. (25 marks)
Question 1c
Recommend to Grayson management on the product mix for two types of shelves. Comment on the role of fixed overhead cost in the optimal solution. (5 marks)
Hire a Professional Essay & Assignment Writer for completing your Academic Assessments
Question 2
Executives at PharmaPro Solutions have decided to establish a new production facility for the company’s top-selling cholesterol medication. The challenge now lies in determining the facility’s optimal size (in terms of production capacity). Last year, the company sold 960,000 units of this medication at a price of $14 per unit. They anticipate the demand for the medication to follow a normal distribution, with the mean increasing by approximately 45,000 units per year over the next 10 years and a standard deviation of 25,000 units. The price of the medication is expected to increase annually with inflation at a rate of 2.5%.
The variable production cost is currently $9 per unit and is also projected to increase with inflation at the same rate. Other operating costs are estimated at $2 per unit of capacity in the first year of operation, with inflationary increases in subsequent years.
The construction cost of the facility is projected at $18 million for a baseline capacity of 1 million units per year. Additional capacity above this level can be added at a cost of $10 per unit of extra capacity. Assume the company pays for the facility at the time of its completion, while all other cash flows occur at the end of each year. The company applies a 12% discount rate to cash flows for its financial decisions.
Question 2a
Construct a spreadsheet model to calculate the net present value (NPV) for this project for a given capacity. Identify the variable and show the setting needed. Make any assumptions where necessary. (25 marks)
Question 2b
What is the expected NPV for a facility with a production capacity per year of 1,000,000 + X*100,000 units, (where X is the last digit of your PI number) per year? (5 marks)
Question 2c
Determine what is the best capacity that provides the highest NPV for the given. You should consider various values of the capacities (at least 10). Show the output charts. (10 marks)
Question 2d
Calculate the facility’s capacity that will ensure a 90% probability of achieving a positive NPV for this investment. You should consider various values of the capacities (at least 10). (10 marks)
Buy Custom Answer of This Assessment & Raise Your Grades
- Final Assignment: Migrating FashionOnline’s Infrastructure to AWS: A Strategy for Enhanced Availability and Data Protection
- HRM331: Talent Management – Strategic Shift from the War for Talent to the Wealth of Talent
- Marginalised Populations – The Structural and Cultural Exclusion of People Experiencing Homelessness in Singapore
- CVEN3501 Assignment 2: Groundwater Modelling of Drawdown from a Pumping Bore
- CSCI312 Assignment 2: Conceptual Modelling and Implementation of a Data Warehouse and Hive Queries
- CH2123 Assignment: Fugacity, VLE Modeling & Applications of Henry’s Law
- BAFI1045 Assignment -Constructing and Evaluating Passive and Active Portfolios Based on the Straits Times Index (STI)
- FIN2210E/FIN2212E Group Assignment: Financial Risk Management Analysis of Bursa Malaysia Companies
- FLM101 Assignment: A Film Analysis: Stylistic Techniques and Their Thematic Importance
- HRM Assignment Answer: Talent Transformation in the Age of AI: Turning Challenges into Opportunities via Ecosystem Innovation
UP TO 15 % DISCOUNT

